Capture Tags with OpenTelemetry
15 minutesLet’s add some tags to our traces, so we can find out why some customers receive a poor experience from our application.
Identify Useful Tags
We’ll start by reviewing the code for the credit_check function of creditcheckservice (which can be found in the /home/splunk/workshop/tagging/creditcheckservice/main.py file):
@app.route('/check')
def credit_check():
customerNum = request.args.get('customernum')
# Get Credit Score
creditScoreReq = requests.get("http://creditprocessorservice:8899/getScore?customernum=" + customerNum)
creditScoreReq.raise_for_status()
creditScore = int(creditScoreReq.text)
creditScoreCategory = getCreditCategoryFromScore(creditScore)
# Run Credit Check
creditCheckReq = requests.get("http://creditprocessorservice:8899/runCreditCheck?customernum=" + str(customerNum) + "&score=" + str(creditScore))
creditCheckReq.raise_for_status()
checkResult = str(creditCheckReq.text)
return checkResultWe can see that this function accepts a customer number as an input. This would be helpful to capture as part of a trace. What else would be helpful?
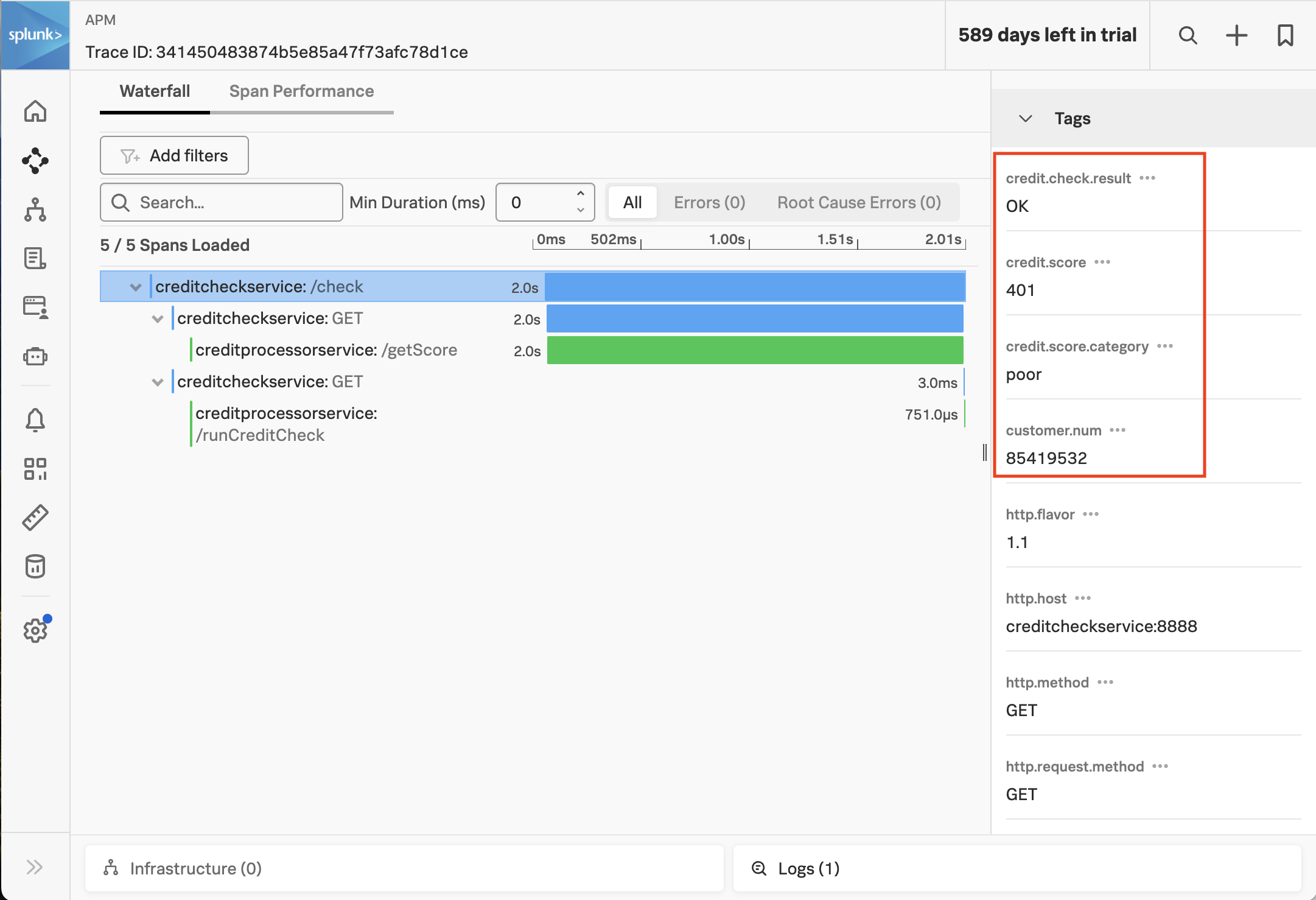
Well, the credit score returned for this customer by the creditprocessorservice may be interesting (we want to ensure we don’t capture any PII data though). It would also be helpful to capture the credit score category, and the credit check result.
Great, we’ve identified four tags to capture from this service that could help with our investigation. But how do we capture these?
Capture Tags
We start by adding importing the trace module by adding an import statement to the top of the creditcheckservice/main.py file:
import requests
from flask import Flask, request
from waitress import serve
from opentelemetry import trace # <--- ADDED BY WORKSHOP
...Next, we need to get a reference to the current span so we can add an attribute (aka tag) to it:
def credit_check():
current_span = trace.get_current_span() # <--- ADDED BY WORKSHOP
customerNum = request.args.get('customernum')
current_span.set_attribute("customer.num", customerNum) # <--- ADDED BY WORKSHOP
...That was pretty easy, right? Let’s capture some more, with the final result looking like this:
def credit_check():
current_span = trace.get_current_span() # <--- ADDED BY WORKSHOP
customerNum = request.args.get('customernum')
current_span.set_attribute("customer.num", customerNum) # <--- ADDED BY WORKSHOP
# Get Credit Score
creditScoreReq = requests.get("http://creditprocessorservice:8899/getScore?customernum=" + customerNum)
creditScoreReq.raise_for_status()
creditScore = int(creditScoreReq.text)
current_span.set_attribute("credit.score", creditScore) # <--- ADDED BY WORKSHOP
creditScoreCategory = getCreditCategoryFromScore(creditScore)
current_span.set_attribute("credit.score.category", creditScoreCategory) # <--- ADDED BY WORKSHOP
# Run Credit Check
creditCheckReq = requests.get("http://creditprocessorservice:8899/runCreditCheck?customernum=" + str(customerNum) + "&score=" + str(creditScore))
creditCheckReq.raise_for_status()
checkResult = str(creditCheckReq.text)
current_span.set_attribute("credit.check.result", checkResult) # <--- ADDED BY WORKSHOP
return checkResultRedeploy Service
Once these changes are made, let’s run the following script to rebuild the Docker image used for creditcheckservice and redeploy it to our Kubernetes cluster:
./5-redeploy-creditcheckservice.shConfirm Tag is Captured Successfully
After a few minutes, return to Splunk Observability Cloud and load one of the latest traces to confirm that the tags were captured successfully (hint: sort by the timestamp to find the latest traces):
Well done, you’ve leveled up your OpenTelemetry game and have added context to traces using tags.
Next, we’re ready to see how you can use these tags with Splunk Observability Cloud!