Application Performance Monitoring Overview
5 minutesSplunk APM provides a NoSample™ end-to-end visibility of every service and its dependency to solve problems quicker across monoliths and microservices. Teams can immediately detect problems from new deployments, confidently troubleshoot by scoping and isolating the source of an issue, and optimize service performance by understanding how back-end services impact end users and business workflows.
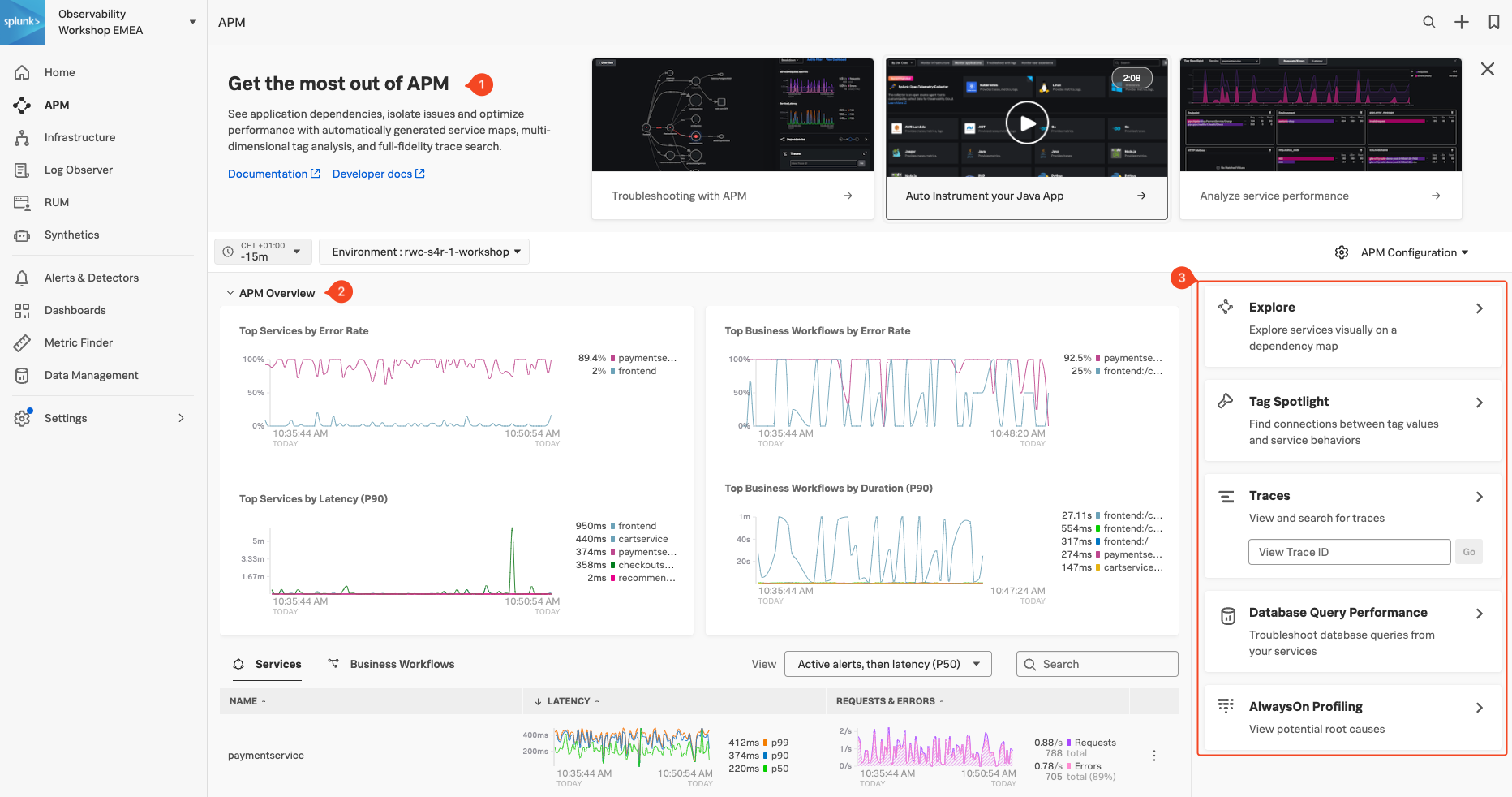
Real-time monitoring and alerting: Splunk provides out-of-the-box service dashboards and automatically detects and alerts on RED metrics (rate, error and duration) when there is a sudden change.
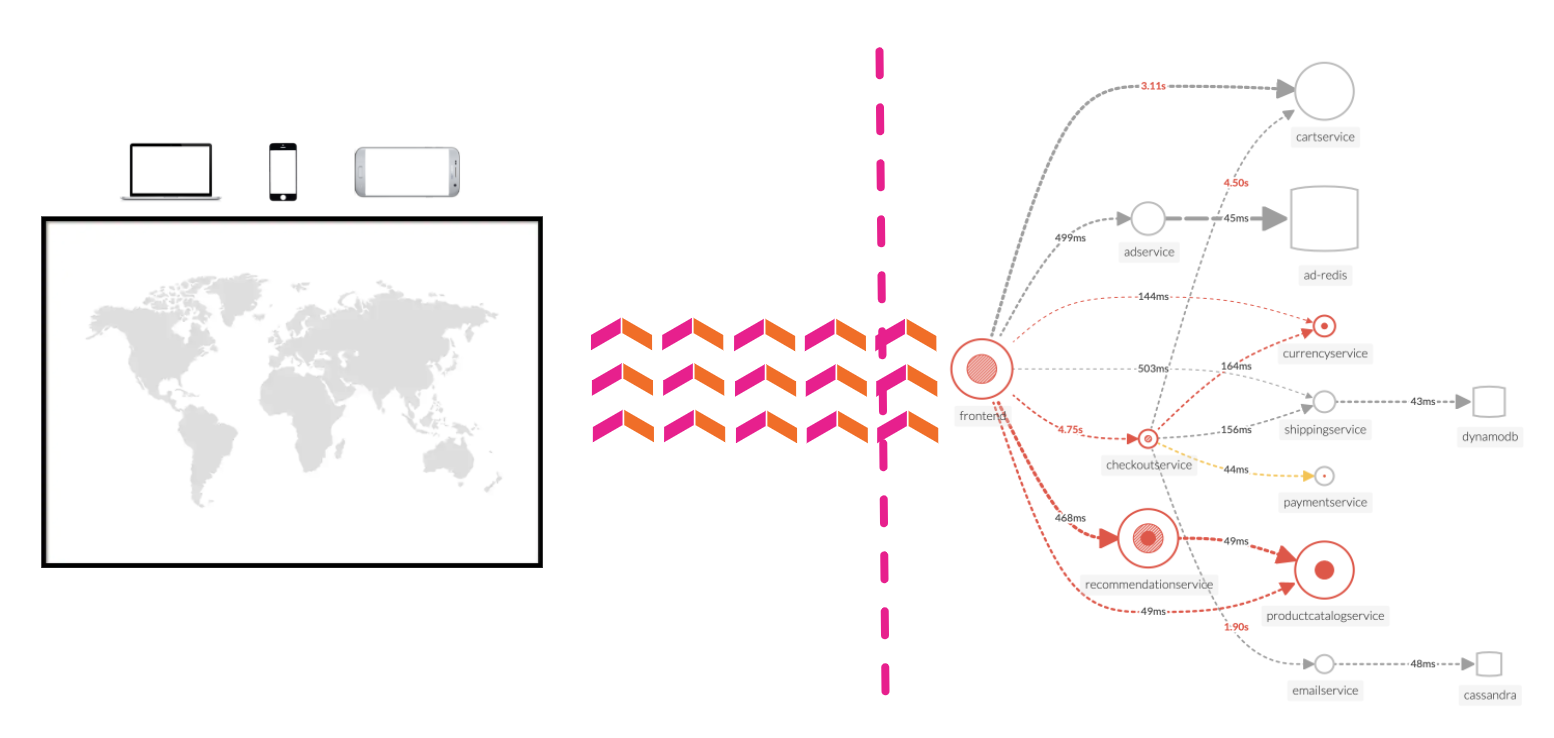
Dynamic telemetry maps: Easily visualize service performance in modern production environments in real-time. End-to-end visibility of service performance from infrastructure, applications, end users, and all dependencies helps quickly scope new issues and troubleshoot more effectively.
Intelligent tagging and analysis: View all tags from your business, infrastructure and applications in one place to easily compare new trends in latency or errors to their specific tag values.
AI-directed troubleshooting identifies the most impactful issues: Instead of manually digging through individual dashboards, isolate problems more efficiently. Automatically identify anomalies and the sources of errors that impact services and customers the most.
Complete distributed tracing analyses every transaction: Identify problems in your cloud-native environment more effectively. Splunk distributed tracing visualizes and correlates every transaction from the back-end and front-end in context with your infrastructure, business workflows and applications.
Full stack correlation: Within Splunk Observability, APM links traces, metrics, logs and profiling together to easily understand the performance of every component and its dependency across your stack.
Monitor database query performance: Easily identify how slow and high execution queries from SQL and NoSQL databases impact your services, endpoints and business workflows — no instrumentation required.